Absolutely! Here’s a comprehensive article about football offensive positions, broken down with headings instead of list items, as requested.
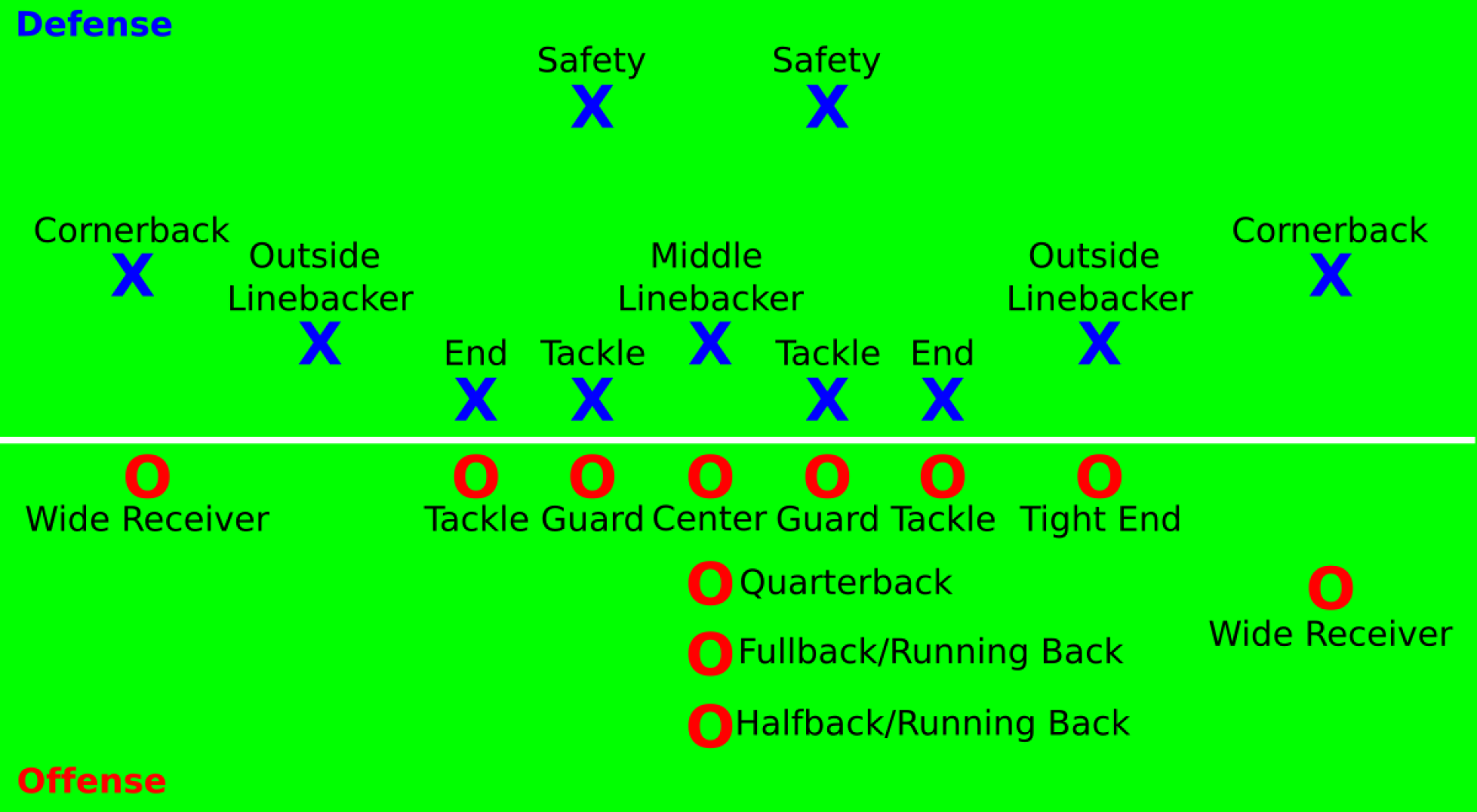
Football, at its core, is a game of strategy, power, and precision. Nowhere is this more evident than on the offensive side of the ball. The offense’s primary goal is to move the ball down the field and score, whether through passing, running, or kicking. To achieve this, a complex choreography of specialized positions works in unison, each player contributing unique skills and responsibilities. Let’s dissect these positions and understand their pivotal roles in creating a formidable offensive machine.
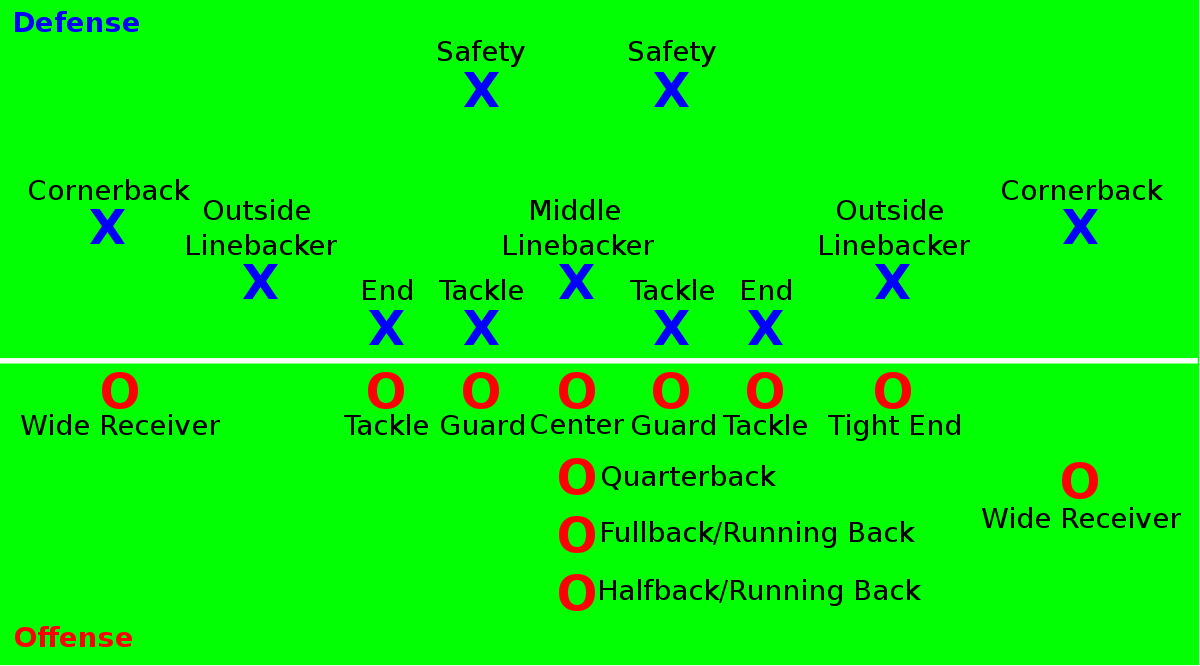
The quarterback is the undisputed leader of the offense, the on-field general who directs the play. He’s responsible for calling plays in the huddle, analyzing defenses, and executing passes or handoffs. The quarterback’s skill set is multifaceted, requiring:
Passing Accuracy: Delivering the ball to receivers with precision and timing.
The quarterback’s ability to process information quickly and accurately is paramount. He must understand the playbook, anticipate defensive movements, and react accordingly. Modern offenses often feature quarterbacks with a blend of passing prowess and running ability, making them dual threats.

The running back is the primary ball carrier in the running game. Their role is to gain yards by running with the football, often through or around defenders. Running backs are categorized into different types:
Feature Backs: These are the primary running backs, carrying the bulk of the workload. They possess a combination of power, speed, and agility.
Key attributes for a running back include:
Vision: Identifying running lanes and anticipating defensive movements.
The running back provides a crucial balance to the offense, complementing the passing game and controlling the clock.
Wide receivers are the primary pass catchers on the offense. They line up wide on the field, running routes to get open for passes from the quarterback. Their role requires:
Speed and Agility: Running precise routes and creating separation from defenders.
Wide receivers come in various sizes and skill sets:
Possession Receivers: These receivers excel at catching short and intermediate passes, often in traffic.
The wide receiver corps provides the quarterback with a variety of targets, creating a dynamic passing attack.
The tight end is a hybrid position, combining the blocking responsibilities of an offensive lineman with the pass-catching abilities of a wide receiver. They line up on the end of the offensive line, providing:
Blocking: Protecting the quarterback and creating running lanes.
The tight end’s versatility makes them a valuable asset to the offense. They can be used as a reliable target in the passing game or as a key blocker in the running game.
The offensive line is the foundation of the offense, protecting the quarterback and creating running lanes for the running back. These players are the unsung heroes, often overlooked but essential to the offense’s success. The offensive line consists of five positions:
Center (C): The center is the leader of the offensive line, snapping the ball to the quarterback and making blocking calls.
Key attributes for an offensive lineman include:
Strength: Blocking defenders and creating running lanes.
The offensive line’s ability to work as a cohesive unit is crucial. They must communicate effectively and execute their blocking assignments with precision.
Modern offenses are constantly evolving, incorporating new strategies and utilizing players in innovative ways. For example:
H-Backs: Hybrid players who combine the roles of a tight end and fullback, providing versatility in blocking and receiving.
The constant evolution of offensive strategies ensures that football remains a dynamic and exciting sport.
The success of a football offense hinges on the collective effort of each position, from the quarterback’s leadership to the offensive line’s physicality. Each player contributes unique skills and responsibilities, working in unison to achieve the ultimate goal: scoring points. Understanding the intricacies of these positions provides a deeper appreciation for the complexity and artistry of offensive football.